Electric turbine: characteristics, principle of operation, pros and cons of work, do-it-yourself installation tips and owner reviews
With tightening environmental regulations, automakers are being forced to develop ways to improve the environmental friendliness and efficiency of engines while maintaining performance. In this regard, forced induction systems have become widespread. Whereas in the past they were used to improve productivity, they are now being used as a means of improving economy and environmental friendliness. Thanks to supercharging, you can achieve the same performance as on atmospheric engines, with fewer cylinders and a smaller volume. That is, supercharged engines are more efficient. Another method is the use of electrical energy both separately (electric motors) and in combination with internal combustion engines (hybrid power plants). This article discusses electric turbines that combine these approaches.
General features
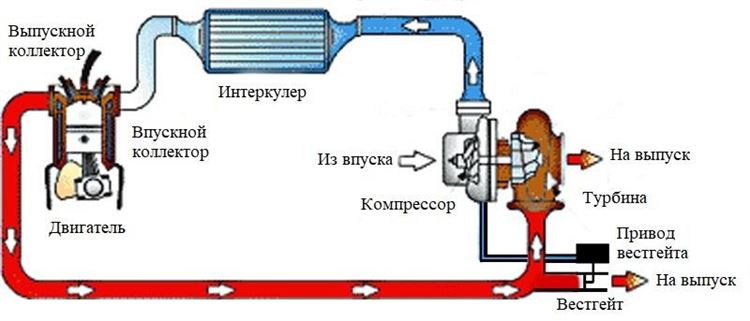
Non-electric systems of forced induction according to the energy source are classified into turbochargers and superchargers. Electrical systems build on them and aim to improve transient performance and minimize lag.
An electric blower, according to Honeywell, is a compressor driven by an electric motor that is mounted on a supercharged motor. That is, this is an additional device for a turbo engine. An electric turbine is an analogue of a mechanical turbine. The drive in this case can be implemented in different ways.
According to the classification of researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, electrical systems of forced induction are differentiated by design and principle of operation into the following types:
- electric superchargers (EC/ET/ES);
- turbines with electric assistant (EAT);
- electrically separated turbines (EST);
- turbines with additional electrically driven compressor (TEDC).
Design
The above types of electric turbines have a different device. This is in different layouts of components, in differences in their technical parameters, etc.
EC
EC is a compressor driven by an electric motor. This is the electric blower mentioned above. The electric drive provides the greatest control flexibility and the ability to operate the compressor at the optimum operating point. However, this requires powerful electrical components.
EAT
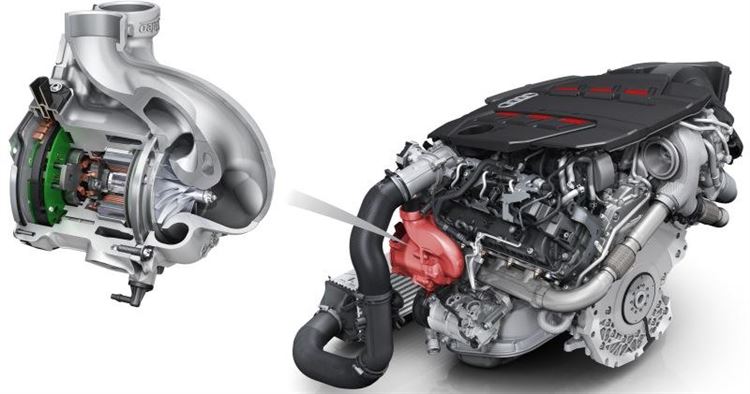
In EAT, a high-speed electric motor is mounted between the turbine and compressor, usually on a shaft. Due to the fact that it is not the main source of energy, low power electrical components are used. This results in a low cost. In addition, such turbochargers have the ability to self-detect the position of the rotor and are characterized by good generating and motoring capabilities. The main problem is the high temperature effect on the electric motor, especially if it is installed inside the housing.
There are various methods for solving it. For example, BMW installed clutches to allow the electric motor to be connected and disconnected from the shaft. Thanks to this, the motor can be placed outside the turbine. G+L inotec used a permanent magnet motor with a large air gap, which can also be located outside. The inner diameter of the stator is equal to the outer diameter of the compressor, and the outer diameter of the rotor is equal to the output diameter of the shaft. The air gap may act as an air inlet. This provides advantages in terms of cooling, inertia and thermal effect. In addition, in terms of thermal stability and thermal control, induction electric motors with variable magnetic resistance, universal collector ones are more preferable in comparison with a motor with surface permanent magnets.
IS
In EST, the turbine and compressor are not connected by a shaft, and each of them is equipped with an electric motor. This allows the compressor and turbine wheels to operate at different speeds. This design has similar advantages to ET, but, unlike it, is able to generate energy. In addition, it is characterized by a smaller temperature effect due to the separation of the compressor and turbine, as well as the absence of additional inertia from the turbine and its shaft. Separating the turbine and compressor is advantageous from a packaging point of view, as it allows the air flow path to be optimized. However, this technology also requires a powerful electric motor, generator and inverters to meet the torque/inertia ratio, which comes at a cost.
TEDC
The TEDC is a mechanical turbine with an additional compressor driven by an electric motor. According to the location of the compressor relative to the turbine, these systems are classified into options upstream and downstream (above and below the turbine, respectively). In general, they are characterized by significantly better responsiveness during transients at the "bottom" due to the independence of the electric motor from the inertia of the turbine and shaft. Moreover, downstream TEDCs are superior in this regard to upstream options due to the fact that the latter are characterized by a large volume to maintain pressure. Another advantage of electric turbines of this type is the minimal differences from mechanical ones.
Operating principle
The above types of electric turbines differ in the principle of operation. So, the drive is implemented in different ways, some of them are able to generate energy, etc.
EC
In EC, the compressor is driven by an electric motor. Such a system is not capable of generating energy, but can be combined with a regenerative braking system or an integrated starter generator to store it.
EAT
In EAT, at low speeds, the electric motor provides additional torque to the compressor to increase boost pressure. At the "tops" it generates energy that can be transferred to storage. In addition, the electric motor can prevent the turbine from exceeding its speed limit. However, a high back pressure effect may occur, which compensates for the energy extracted from the exhaust gases.
Due to the possibility of generating electricity from exhaust gases, such turbochargers are called hybrid. On passenger cars, depending on the driving cycle, they can generate from several hundred watts to kW. This allows you to replace the generator, saving fuel.
IS
In EST, the energy of the exhaust gases does not drive the compressor directly, but is converted into electrical energy using a generator. The compressor is driven by stored energy.
TEDC
In TEDC, the electric motor functions independently of the turbine, and the additional compressor driven by it serves to increase boost at the "bottom".
Structural and functional differences
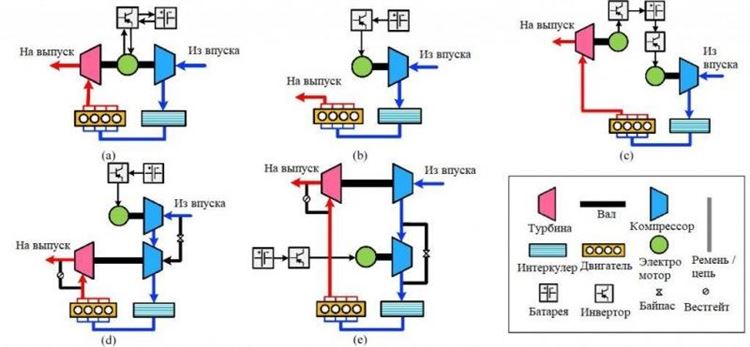
The fundamental differences between the considered electrical systems of forced induction are combined by researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison in graphical and tabular form. The figure below shows the diagrams of their device (a – EAT, b – EC, c – EST, d – TEDC upstream, e – TEDC downstream).
The table reflects the main provisions of the device. These include the source of energy, the drive of the compressor, the power of the electrical components. In addition, qualities such as dimensions and temperature effect are important.
In terms of durability, according to IHI, electric turbines will be equivalent to mechanical ones due to operation in the same conditions in a more gentle mode with greater design complexity.
Relevance
Despite good performance, electric turbines are not currently widely used on mass-produced cars. This is due to their high cost and complexity. In addition, improved versions of mechanical turbines (twin scroll and variable geometry) have similar advantages over the initial modifications (albeit to a lesser extent) at a much lower cost. Now EST uses Ferrari in the Formula 1 engine. According to Honeywell, the mass use of electric turbines will begin at the beginning of the next decade. It should be noted that electric superchargers are already used on some production cars, such as the Honda Clarity, as they are simpler.
The simplest and homemade mechanisms
At the beginning of the decade, the simplest cheap mechanisms appeared on the market, like computer coolers, also called electric turbines. They are located on the inlet and are battery operated. It is possible to use such electric turbines both on the carburetor and on the injector. According to manufacturers, they increase the flow of air entering the engine, accelerating it, which gives a performance increase of up to 15%. In this case, the parameters (revs, flow, power) are usually not indicated. It is very easy to install such electric turbines on a car with your own hands.
However, in reality, their electric motors develop up to several hundred watts, which is not enough to increase the volume of flow, since this requires about 4 kW. Therefore, such a device will become a serious obstacle at the inlet, as a result of which, on the contrary, productivity will be reduced. At best, the losses from it will be small, which will not significantly affect the dynamics.
In addition, on the Internet you can find developments on creating an electric turbine with your own hands. Unlike the cheap options mentioned above, they are built on the basis of a centrifugal compressor and a brushless motor with a power of up to 17 kW and a voltage of 50-70 V, since only such a motor is able to provide sufficient torque and speed to rotate the compressor. The motor must be equipped with a speed controller. This system does not require an intercooler – a cold intake is enough for it. The installation of an electric turbine of this type may require the replacement of a generator (for 90-100 A) and a battery (for a more capacious one with a high current output). The rotation speed of the compressor is determined by the position of the throttle. Moreover, the dependence is not linear, but exponential.
It is advisable to create such electric turbines for cars with small engines up to 1.5 liters, due to high energy consumption. Moreover, the larger the volume of the engine, the less boost pressure the supercharger can create. So, on a 0.7-liter engine, it will be 0.4-0.5 bar, on a 1.5-liter engine – 0.2-0.3 bar. In addition, such a supercharger will not be able to function for a long time at maximum performance due to heating. However, the controller can be configured to force activation.
Due to the high cost of the components, it is very expensive to make such an electric turbine. Reviews indicate a tangible increase in performance.
In terms of design, these mechanisms, like the cheap options mentioned above, are electric superchargers. However, they are often erroneously referred to as electric turbines. Now on the market there are more serious branded mechanisms that are close to home-made.
Summary
Electric turbines are more responsive, productive and efficient than mechanical ones and have additional features. At the same time, on the one hand, they have a complicated design, but, on the other hand, they operate in more gentle conditions.
| Type | EC | EAT | IS | TEDC | |
| Energy source | Battery | Exhaust gases / battery | Exhaust gases / battery | Exhaust gases / battery | |
| Electric motor and inverter power | high | Low | high | Low | |
| temperature effect | Short | Tall | Short | Short | |
| The size | Small | Average | Large | Large | |
| Electric turbine | Not | Yes | Yes | Not | |
| Turbo-electric compressor drive | Not | Yes | Not | Not | |
| Type | EC | EAT | IS | TEDC upstream | TEDC downstream |
| Advantages |
|
|
|
|
|
| disadvantages |
|
|
|
|
|